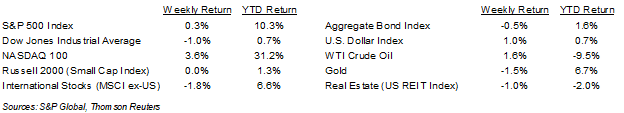
Last week ended without a debt ceiling deal, but negotiations over the weekend finally yielded an agreement between the parties. The S&P 500 Index ended the week +0.3%, the Dow was -1.0%, and the NASDAQ was +3.0%. The 10-year U.S. Treasury note yield increased to 3.820% at Friday’s close versus 3.692% the previous week.
House Speaker Kevin McCarthy and President Biden reached a deal on suspending the debt ceiling through January 2025 with several points from the original bill the House passed in April. The bill still needs to pass the House and Senate this week. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen revised her deadline date to June 5th before the federal government may run too low on funds to meet all current obligations.
Outside of the votes on the debt ceiling agreement, the major item on the calendar this week is the May employment report scheduled for Friday. Despite the distracting drama of the debt ceiling negotiations, the economy likely remains too strong for the Federal Reserve and the odds of a 0.25% increase at the June 14th Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting has moved up to 66.4% from 25.7% a week ago.
The first quarter earnings season reporting period is almost complete. To date, 485 companies in the S&P 500 Index have reported first quarter earnings and an additional nine companies scheduled for this week. For the first quarter, the S&P 500 Index is expected to see earnings decline 0.1% on revenue growth of 3.6%. The outlook for the quarter has continuously improved since the start of earnings season several weeks ago when consensus was a 5.2% earnings decline on revenue growth of 1.6%. For full year 2023, S&P 500 Index earnings are expected to grow 1.5% on revenue growth of 1.8%.
In our Dissecting Headlines section, we look at the components of the debt ceiling agreement.
Financial Market Update
Dissecting Headlines: Debt Ceiling Agreement
House Speaker Kevin McCarthy and President Biden announced an agreement on a debt-ceiling deal. It still requires passage by the House and Senate and those votes likely happen mid-week.
The deal suspends the debt ceiling through January 2025 before another debt-ceiling increase would need congressional approval. This pushes the issue beyond the 2024 election. In exchange, there is a limit on discretionary spending to be roughly flat in 2024 versus 2023, excluding defense, and growth of 1% the year after. The bill also requires Congress to approve 12 annual spending bills or face a snapback to spending limits from the previous year, which would mean a 1% cut.
The bill would rescind approximately $30 billion in unspent COVID relief money. It would also rescind about $10 billion of the $80 billion that had been allocated to the IRS. It also raises some work requirements for individuals to receive assistance under the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP).
New energy projects would be placed under a single lead agency to help speed up environmental reviews. The bill also ends the pause on student debt repayment and keeps the cancellation proposal legality with a pending decision by the Supreme Court. A repeal of clean energy sector tax credits did not make it into the final bill.
________________________________________
Want a printable version of this report? Click here: NovaPoint Weekly May 29, 2023
To learn more about these topics and our investment strategies, call us at 404-445-7885 or contact us here.
Do you understand your personal investment risk tolerance and the risk of your current portfolio? You can learn these by taking our Risk Analysis Questionnaire.
